
WHAT IS WEB 3.0? INTERNET NEXT BIG THING
Web 3.0 is heard everywhere, no matter what resource you go to, what forum you open, and any social media platforms… New buzzword – this is how people who do not share the general enthusiasm speak about Web 3 with a slight touch of disdain. However, they are clearly in the minority. Everyone talks about it with enthusiasm; they see the future behind it.
Web 3.0 is followed by blockchain, cryptocurrencies, non-fungible tokens (NFT), and many more terms that make your head spin if you are not in the loop. And, of course, you have to be familiar with the matter! We don’t know precisely how long Web 3.0 will last or if Web 4.0 will replace it. However, without understanding the general principles of technology, your business will not last long.
What is Web3? The Decentralized Internet of the Future Explained
At one time, the World Wide Web blew up the “market” of information online, which now, located on the network, could be available to anyone with the Internet, anywhere on the planet. Web 2.0, in turn, has radically changed the principles of communication. And Web 3.0 is more about values and meanings. Web 2 is an interface revolution, and Web 3 is a backend revolution.
The term Web 3.0 itself originated in 2014. Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood created it. Simply put, Web 3.0 is a decentralised way of communicating on the Internet instead of the centralized storage that Web 2.0 offers. This significantly increases the level of security and safety of personal data. And all this is possible thanks to the blockchain system.

What is Blockchain
Blockchain is a database that is different from other similar decentralized networks. It does not have a single owner who could use the information stored there at his discretion by right of ownership. Instead, the participants collectively manage the blockchain database, and it is available to anyone. At the same time, stealing this surface data has become much more difficult.
The idea is that everything you do, from shopping to social media, is handled through the same secure processes, providing both more privacy and more transparency.
The blockchain system uses the principle of cryptography for protection – information is stored in blocks, which, to form a single whole, line up in a chain. Hence the name. In order to somehow distinguish between blocks, each of them has its own timestamp, data, and a hash pointing to the content.
These shares can be managed by people who have enough tokens or crypto. If you have enough of these tokens, you have the right to vote on the network. Governance token holders can spend their assets to vote on, for example, the future of the decentralized lending protocol.

What is Web3 in Crypto?
When you hear about web3, you will notice that cryptocurrencies are often part of the conversation. This is because cryptocurrency plays a significant role in many of these protocols. In addition, it provides a financial incentive (tokens) for anyone who wants to create, manage, contribute to or improve one of the projects.
These protocols can offer many services:
- Calculations
- Storage
- Bandwidth
- Identification
- Hosting
Service consumers typically pay to use the protocol, similar to paying a cloud service provider today.
Cryptocurrencies have created a robust market for decentralized finance (Defi), which is only growing every year. Web3 applications are often based on a technology called Ethereum, which, like bitcoin, rewards users who help maintain its network. This coin is called Ether, which has a total market value of $511 billion.
The apps themselves can also have linked tokens that can not only pay for services, but also act as voting shares that govern the development of the apps, and even the fee structure.

What is a Web3 app?
Web3 applications run either on blockchains or in decentralized networks consisting of many peer nodes (servers) or in a combination, forming a crypto-economic protocol. These are decentralized apps.
At the heart of Web3 are distributed applications (or dApps) built using the Ethereum blockchain that pay users to help keep it online. Dapps play the same role for Web 3.0 that the App Store has played for the Apple ecosystem so far.
More than 8,700 active decentralized applications are registered on the DappRadar tracker. They include many crypto trading platforms and games. Sometimes the line between the two is blurred: many games involve winning and trading non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, virtual characters, or collectibles that can cost sky-high prices.
Most decentralized apps are now used for a cryptocurrency exchange or NFT trading. A small percentage of dApps are games that can be played to earn money in cryptocurrency.
Web3 and NFT
Speaking of games… In Web 2.0 iteration, gamers can only resent the number of bugs in the next sequel to their favorite game. With Web 3.0, users can vote on the necessary changes with their tokens and, in fact, build the game as they like. NFT is also on the wave in the gaming industry. Game fans are buying up items placed in virtual reality.
And in general, now a musical composition or a picture in a museum, as well as any meme, and even your cat, can become tokenized. So, one of the notorious NFT Rare Bored Ape Yacht Club was sold in 2021 for $3.4 million!
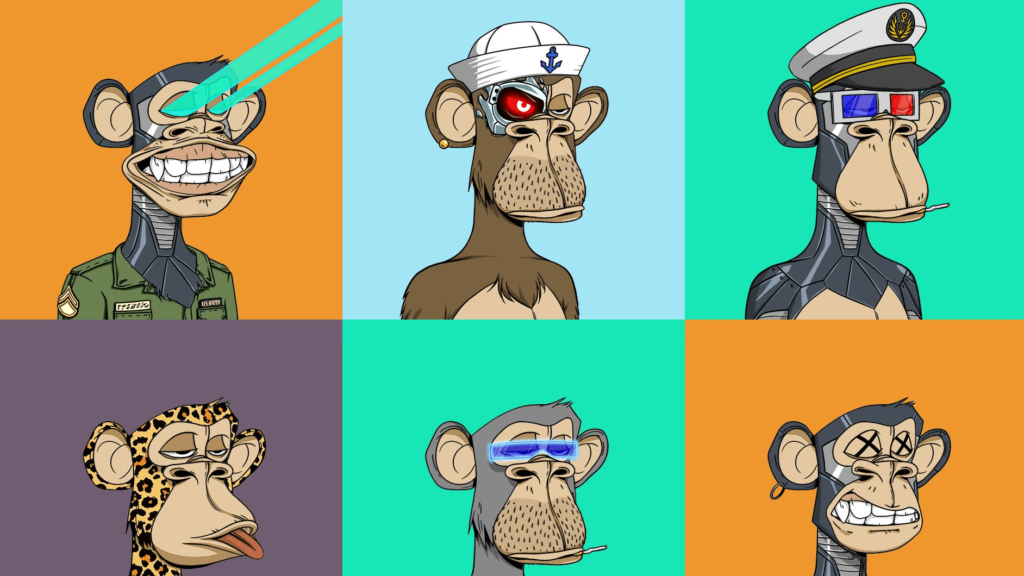

If earlier venture capitalists participated in developing a game (and, in general, any other product) with their own money, who dictated to the creators the conditions under which profit would be possible in the shortest possible time, now anyone can financially participate in the development. The company announces the release of x number of tokens, gives 10% to early investors, puts up 10% for sale, and saves the rest for future payments to contributors and project financing.
Someone will probably think this principle is too similar to a financial pyramid. However, all blockchain data is entirely public and open, and buyers have complete transparency about what is happening. At the same time, network marketing companies that do not shun fraud keep everything a secret.
Web 3.0: Prospects, Issues, and Challenges
The idea of a decentralized internet looks attractive. We immediately imagine freedom from the “oppression of the capitalists” who monopolize entire areas of our daily lives. However, not everything is so rosy.
Who is currently investing in Web 3.0 the most? Venture capitalists, big tech companies, and hedge funds with multi-million dollar capitals. Accordingly, modern blockchain networks are unevenly distributed. In other words, the encryption keys for multi-million dollar sums are in the hands of just a few large investors. It’s just that information is now stored in more than one place, which is really much more difficult to control. Still, if at the same time you hire a lot of figureheads who will be participants in the decentralization scheme, then the whole idealistic principle comes to naught.
Some experts go further, arguing that Web 3.0 is the same centralized organization, just with a different name. Needing no introduction, Elon Musk says Web3 is more of a “marketing buzzword” than reality.

It is worth noting that some cybersecurity experts emphasize that although it is more challenging to hack data in the blockchain format, it is also almost impossible to prevent such a hack. After all, the problem is not whether people can easily access it, but whether they know how to manage their data securely. An example of such a problem would be the widespread theft of cryptocurrencies.
Many projects don’t even list contact numbers, although they may support online chat groups. If you accidentally type in a typo and send money to the wrong account, it could be lost forever. You will not be able to solve the problem as if you called the bank’s customer service. After all, if earlier it was the bank that provided the security of your finances, then in Web 3.0 – God helps those who help themselves. With freedom, you get a responsibility that not everyone can handle.
Skeptics believe that many of the requirements underlying Web3, such as distributed architecture and decentralization, are better implemented without blockchains. Since building a decentralized structure based on a centralized one does not radically change anything.
In Conclusion
So, does Web 3.0 technology, which has not yet become firmly established in everyday life, no longer justifies itself? As in any innovative solution, there will always be people who simply want to make money on fraud, but also enthusiasts who will create genuinely amazing things. So, is Web 3.0 a boon or a slightly updated Web 2.0? This will be shown in the next decade. In any case, a lot depends on how the big players behave.
Trident Technolabs always strives to be at the forefront of the latest technology. For us, Web 3.0 is not something from the distant future but a completely unambiguous reality with which our employees work closely. Therefore, if you are interested in developing in the Web 3.0 area – feel free to write!




Leave a comment: